Blockchain Overview
If you have been following banking, investing, or cryptocurrency over the last ten years, you may have become familiar with blockchain, the record-keeping technology behind bitcoin.

What is Blockchain?
In trying to learn more about this, you’ve probably encountered the following definition: “blockchain is a distributed, decentralized, public ledger.”
The good news is, blockchain is actually easier to understand: It is digital information (the “block”) stored in a public database (the “chain”).
Anyone network participant can view the blockchain’s contents, but users can also connect their computers to its network. In doing so, their computer receives a copy of the blockchain that is updated automatically whenever a new block is added.
The fact that each computer in the network has its own copy of the blockchain, translates into thousands, or in the case of Bitcoin, millions of copies of the same blockchain distributed across the world. This, however, does not mean that everyone can see the information stored in the blockchain without proper authorisation. Date stored on blockchain is encrypted and personal information about users is limited to their digital signature or username (a “private key”).
Although each copy of the blockchain is identical, spreading that information across a network of computers makes the information more difficult to manipulate and virtually impossible to tamper with. With blockchain, there isn’t a single, definitive account of events that can be manipulated. Instead, a hacker would need to manipulate every copy of the blockchain on the network.
Blockchain Practical Applications
Due to the noise generated by Bitcoin, most people identify blockchain with its application in electronic monetary transactions.
But it turns out that blockchain is a reliable way of verifying other types of transactions as well. In fact, blockchain technology can be used to store data about property exchanges, stops in a supply chain, and even votes in an election.
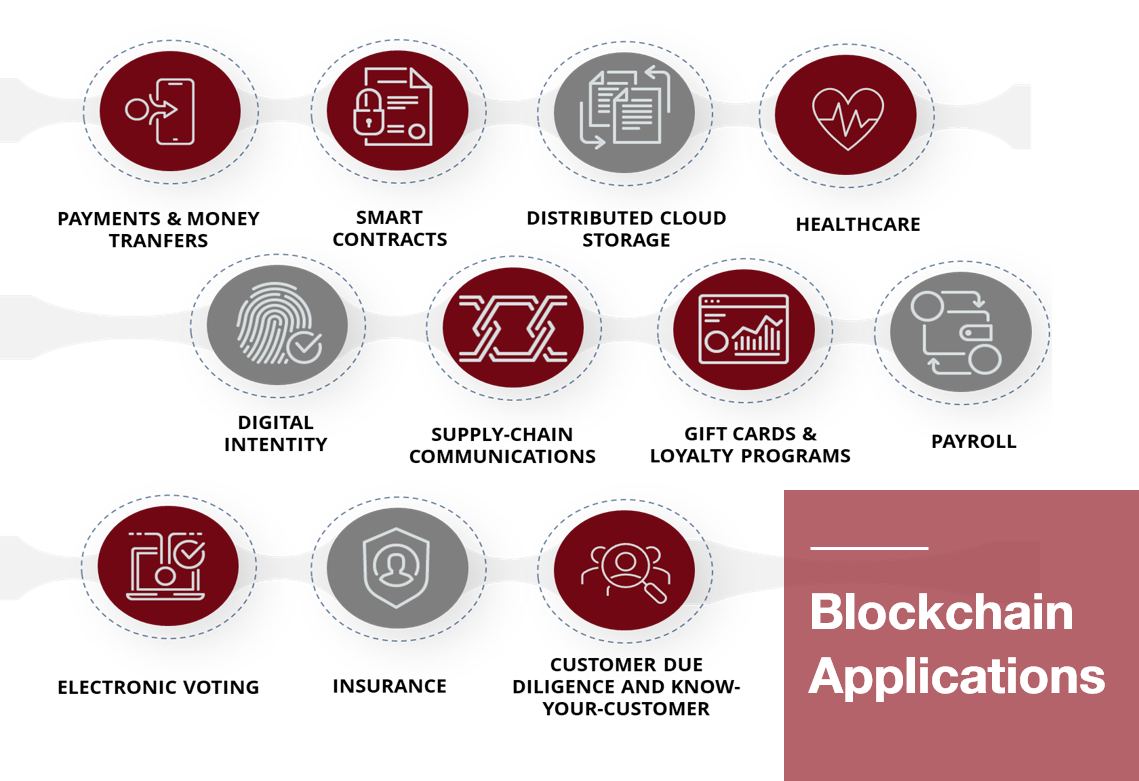

-
Payments & Money Transfers
Blockchain technology’s first successful application was cryptocurrencies, it’s most well well-known application is being able to send and receive payments.
Blockchain enables the instant, direct and secure transfer of funds, to anyone we want in the world while keeping fees ultra-low. This is mainly because technology replaces any intermediaries in the equation (such as banks or money remittance service providers), thus, making the transfer and its verification faster, cheaper and safer.

2. Smart Contracts
The term “smart contract”’ is associated with the blockchain thanks to the Ethereum Project.
“Smart contracts” are self-automated computer programs that can carry out the terms of any contract. In simple words, it is a financial security held in escrow by a network that is routed to recipients based on future events and computer code. With “smart contracts” businesses will be able to build regulatory and legal compliance into code, thus lowering transaction costs and increasing reliability. On top of that, the distribution of the “smart contract” throughout the decentralized network render its terms unbreakable.

3. Distributed Cloud Storage
Cloud storage will be another application that businesses can benefit from. Blockchain technology promises affordable, fast, and secure cloud storage.
Healthcare
As in the example of distributed cloud storage, healthcare providers can leverage blockchain to securely store their patients’ medical records. When a medical record is generated and signed, it can be written into the blockchain, which provides patients with the proof and confidence that their record cannot be tampered with or exposed. Personal health records can be encoded and stored on the blockchain, while being accessible only by those who hold their “private key”.

4. Digital Identity
Identity fraud is estimated to cost the global economy billions of dollars annually. Because of that, security should be a top concern for businesses of all sizes.
Blockchain technology make tracking and managing digital identities both secure and efficient, thus, resulting in reduced fraud.
Blockchain technology can solve many digital identity issues, where identity can be uniquely authenticated in an irrefutable, immutable, and secure manner. Current methods use problematic password-based systems of shared secrets exchanged and stored centrally on insecure databases. Blockchain-based authentication systems are offer irrefutable identity verification using digital signatures based on public key cryptography.
With blockchain identity authentication, the only check performed is whether or not the transaction was signed by the correct private key. It is inferred that whoever has access to the private key is the owner, and the exact identity of the owner is deemed irrelevant.
Blockchain technology can be applied to identity applications in areas like IDs, online account login, E-Residency, passports, birth certificates, etc.

5. Supply Chain Communications & Proof of Provenance
Most of the things we buy aren’t made by a single entity, but by a chain of suppliers who sell their components (e.g., graphite for pencils) to a company that assembles and markets the final product.
The problem with this system is that if one of these components fails the brand suffers the consequences. By utilizing blockchain technology, a company could proactively provide digitally permanent, auditable records that show stakeholders the state of the product during each value-added step.

6. Payroll
Since the blockchain has its roots in cryptocurrency, it only makes sense that it could be used as an application to compensate employees. If your company regularly pays wages to international workers, then incorporating a stablecoin into the payroll process could be a major cost saver.
The application of blockchain through the adoption of a native stablecoin will circumvent costly fees associated with transferring money internationally, as well as the time it takes for such funds to move from one bank to another, payments made via electronic money on a blockchain can save both time and money for employers and employees alike. By using a public ledger of all transactions in chronological order you can actually pinpoint the exact location of the funds throughout the process.

7. Electronic Voting
A blockchain-based mobile voting system was used in the U.S. state of West Virginia’s 2018 midterm elections. Following the early November elections, the state’s Secretary of State noted that 144 military personnel stationed overseas from 24 counties were able to successfully cast their ballots on a mobile, blockchain-based platform.
Voting with blockchain carries the potential to eliminate election fraud and boost voter turnout. Each vote would be stored as a block on the blockchain, making them nearly impossible to tamper with. The blockchain protocol would also maintain transparency in the electoral process, reducing the personnel needed to conduct an election and provide officials with instant results. West Virginia billed the experiment as a success and says it plans to use the technology again in 2020. Blockchain-based voting is by no means limited to government elections, but it may apply in any mode of voting and governance.

8. Insurance
Blockchain technology allows for the entire insurance industry to dramatically optimize business processes and minimize insurance fraud by sharing data in an efficient, secure, and transparent manner.
Using blockchain to revolutionize insurance policies shifts systems onto smart contracts operating automatedly on peer-to-peer networks, helping to phase out antiquated pen and paper processes and eliminate red tape the insurance industry is notoriously riddled with.
Moreover, blockchain is already being leveraged by the insurance industry. Organizations such as Swiss Re, Aegon, Allianz, Munich Re and Zurich have launched the Blockchain Insurance Industry Initiative, B3i, which aims to explore the potential of distributed ledger technologies to better serve clients through faster, more convenient and secure services.

9. Customer Due Diligence & Know Your Customer
Regulators have been increasing their pressure on businesses to step up their KYC due diligence, in an effort to combat financial crime. As a result, financial firms had to go on a hiring spree to deal with these regulations.
Blockchain offers a way to address the increased compliance burden, as it allows for a secure, public digital ledger providing almost instantaneous and truly secure verification of identity. Due to the immutable and unchangeable nature of the record kept in the blockchain, fraud risk is substantially minimized.
Blockchain-based KYC has many inherent advantages. Many companies are working on a ‘digital signature’ that would keep a secure copy of all your identity, address or other verification documents stored on a blockchain. Particularly if this is a public blockchain, it would be decentralized, therefore, transparent and secure.
A bank or other financial institution who is looking to verify customer identity would simply need to be given permission to access the personal information, making blockchain KYC incredibly efficient. It would also be standardized, so every financial institution globally – with permission -would be able to share and view the same data.
Updates to personal information would be done on the blockchain, with any institution using the system also being privy to any information changes. Seamlessly, customers could update their personal information across all their accounts simply through their digital signatures. KYC via blockchain would mean that they would not need to contact each institution separately, and institutions would never miss on an update.
Blockchain in KYC is one of the most promising applications of the decentralized technology, serving a real need by decreasing administrative costs and manhours, while increasing security and transparency.
KYC on the blockchain represents a true paradigm shift, pulling away from individual compliance policies wasting talented compliance personnel on repetitive and mundane work.
The Solution
The practical understanding of Blockchain technology and the profound knowledge of the complex legal and compliance legislation applicable, is our added-value service and the basis for the solid legal guidance we provide to our clients in scope of their business needs and strategic goals.
The Idea Stage
We understand the components of your Blockchain Solution and liaise with all competent regulators.

The Compliance Stage
We identify the compliance and legal framework applicable to your particular Blockchain Solution.

The Legal Stage
We answer all your legal questions upon the regulations applicable such as:
- Is your Blockchain Solution regulated or not? What are your obligations and responsibilities?
- Does Blockchain Solution require a passport, notification or authorization or not? Which is the competent authority?
- Does your Blockchain solution meet the regulatory standards of robustness and assurance level under the legal framework applicable?
- Which category of cryptoassets does your cryptoasset fall into, and what does this mean from a regulatory perspective?
The Implementation Stage
We offer a one-stop shop approach and provide a controlled and safe environment:
- We help you set-up your business on a project management basis and assist with the passport, notification or authorization process required
- We provide legal guidance and assist with the assurance and/or service legal assessments required
- We draft the policies and manuals applicable to your Blockchain Solution towards that will govern your business operations
- We follow-up the new rules being implemented in Greece and on an EU level on your Blockchain Solution particularly and provide you with all updated information